Ever since Microsoft launched its first version of operating system in 1985, the Redmond-based tech giant has been dominating the OS market, winning rivals such as Apple Macintosh and Linux. Although some analysts say that Microsoft is losing its dominance in the OS market just like its web browser Internet Explorer in the browser market, but both Windows XP and Vista have shown pretty good results. Coming first in W3Counter’s browser share list (September 2009) is Windows XP (60.06%), followed by Windows Vista (22.39%).
Ever since Microsoft launched its first version of operating system in 1985, the Redmond-based tech giant has been dominating the OS market, winning rivals such as Apple Macintosh and Linux. Although some analysts say that Microsoft is losing its dominance in the OS market just like its web browser Internet Explorer in the browser market, but both Windows XP and Vista have shown pretty good results. Coming first in W3Counter’s browser share list (September 2009) is Windows XP (60.06%), followed by Windows Vista (22.39%).
Wondered how the previous versions of Microsoft Windows look like, and the product line has changed from a GUI product to a modern operating system.? Let’s activate the way back machine and find out the interface and packaging designs of Windows 1.0, Windows 95, Windows XP, etc.
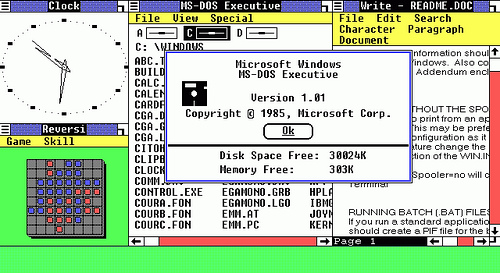
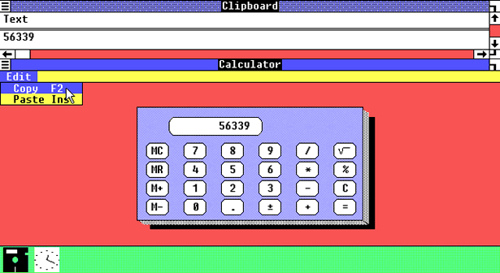
Windows 1.0 (1985)
Released on 20 November 1985, Windows 1.0 was a 16-bit operating system that offers limited multitasking of existing MS-DOS programs and concentrates on creating an interaction paradigm. It was Microsoft’s first attempt to implement a multi-tasking graphical user interface-based operating environment on the PC platform.
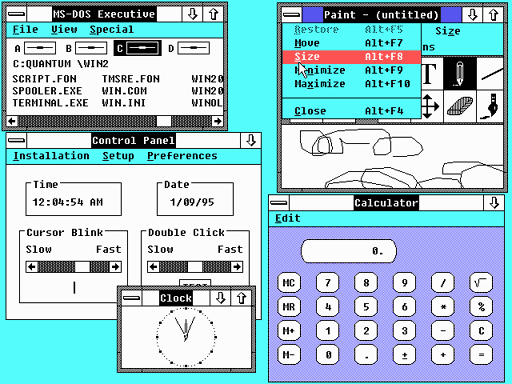
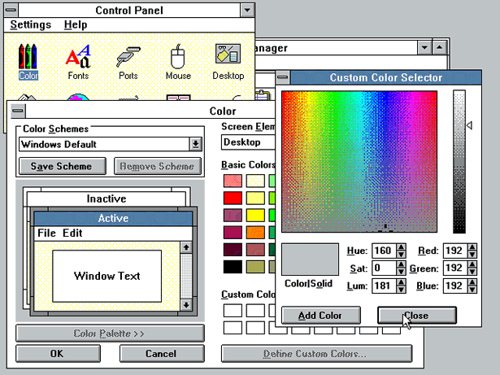
Windows 2.0 (1988)
Windows 2.0 was supplemented by Windows/286 and Windows/386 in 1988. The first Windows versions of Microsoft Word and Microsoft Excel run on Windows 2.0. Windows 2.0 allowed application windows to overlap each other, unlike its predecessor Windows 1.0, which could only display tiled windows. Windows 2.0 also introduced more sophisticated keyboard-shortcuts and the terminology of “Minimize” and “Maximize”, as opposed to “Iconize” and “Zoom” in Windows 1.0.
Windows 3.0 (1990)
Windows 3.0 is the third major release of Microsoft Windows, and was released on 22 May 1990. It became the first widely successful version of Windows and a powerful rival to Apple Macintosh and the Commodore Amiga on the GUI front.
Windows 3.0 succeeded Windows 2.1x and included a significantly revamped user interface as well as technical improvements to make better use of the memory management capabilities of Intel’s 80286 and 80386 processors. Text-mode programs written for MS-DOS could be run within a window (a feature previously available in a more limited form with Windows/386 2.1), making the system usable as a crude multitasking base for legacy programs. However, this was of limited use for the home market, where most games and entertainment programs continued to require raw DOS access.
Windows 3.1x (1992)
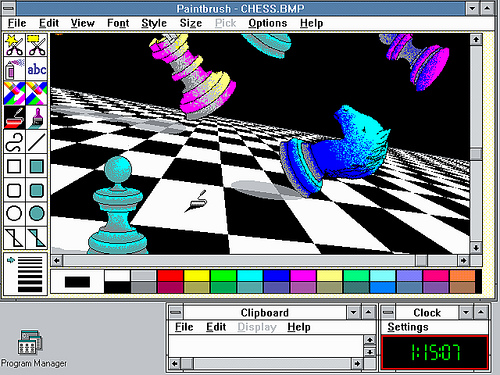
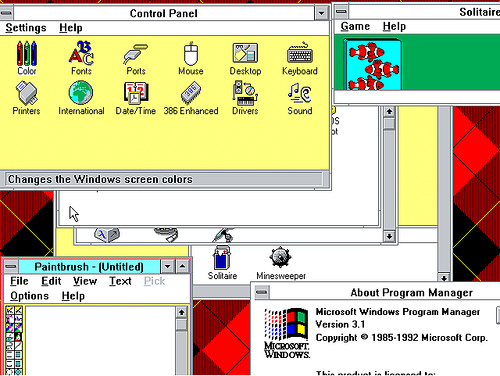
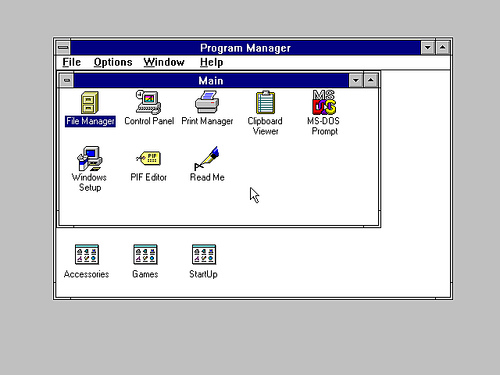
Windows 3.1x is a series of 16-bit operating systems produced by Microsoft for use on personal computers. The series began with Windows 3.1, which was first sold during March 1992 as a successor to Windows 3.0. Further editions were released between 1992 and 1994 until the series was superseded by Windows 95.
Windows 3.1 (originally codenamed Janus, of which two betas were published), released on April 1992, includes a TrueType font system (and a set of highly legible fonts already installed), which effectively made Windows a serious desktop publishing platform for the first time. Similar functionality was available for Windows 3.0 through the Adobe Type Manager (ATM) font system from Adobe.
Windows 3.1 was designed to have backward compatibility with older Windows platforms. As with Windows 3.0, version 3.1 had File Manager and Program Manager, but unlike all previous versions, Windows 3.1 and later support 32-bit disk access, cannot run in real mode, and included Minesweeper instead of Reversi (though Reversi was included in some copies).
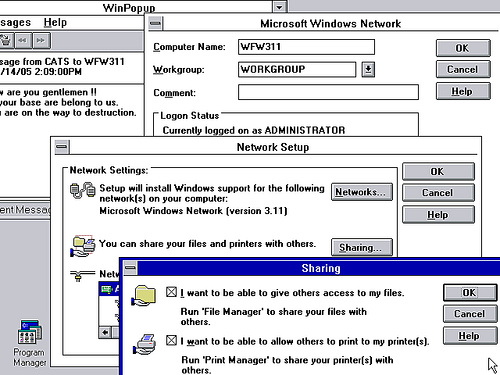
Windows for Workgroups (1992)
Windows for Workgroups is an extension that allowed users to share their resources and to request those of others without a centralized authentication server. It used the SMB protocol over NetBIOS.
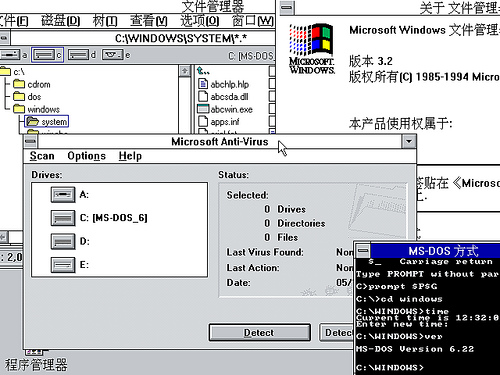
Windows 3.2 (1994)
In 1994, Microsoft released a Simplified Chinese version of Windows for the Chinese market. The updated system identified itself as Windows 3.2. Thus, Windows 3.2 is Windows 3.11 Chinese version. The update was limited to this language version, as it fixed only issues related to the complex writing system of the Chinese language.
Windows 3.2 was generally sold by computer manufacturers with a ten-disk version of MS-DOS that also had Simplified Chinese characters in basic output and some translated utilities.
Windows 95 (1995)
Windows 95 is a consumer-oriented graphical user interface-based operating system. It was released on August 24, 1995 by Microsoft, and was a significant progression from the company’s previous Windows products. It features significant improvements over its predecessor, Windows 3.1, most visibly in the graphical user interface (GUI).
In the marketplace, Windows 95 was a major success, and within a year or two of its release had become the most successful operating system ever produced. It also had the effect of driving other major players in the DOS-compatible operating system out of business, something which would later be used in court against Microsoft.
The basic elements of the interface introduced in Windows 95—including the taskbar, Start button and menu, and the Windows Explorer file manager.
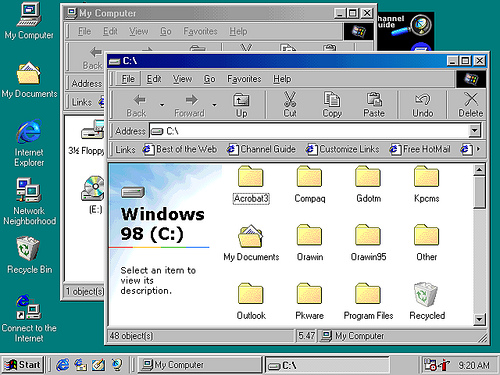
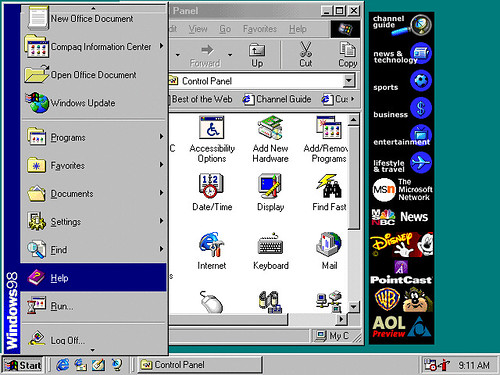
Windows 98 (1998)
Windows 98 (codenamed Memphis) was released on 25 June 1998 by Microsoft and the successor to Windows 95. Like its predecessor, it is a hybrid 16-bit/32-bit monolithic product based on MS-DOS.
Windows 98 Second Edition (often shortened to SE) is an updated release of Windows 98, released on 5 May 1999. It includes fixes for many minor issues, improved USB support, and the replacement of Internet Explorer 4.0 with Internet Explorer 5.0. Also included is Internet Connection Sharing, which allows multiple computers on a LAN to share a single Internet connection through Network Address Translation. Other features in the update include Microsoft NetMeeting 3.0 and integrated support for DVD-ROM drives.
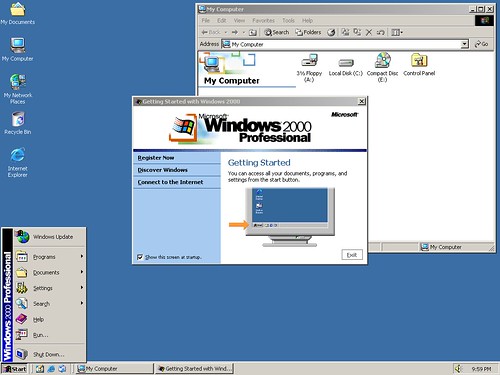
Windows 2000 (2000)
Microsoft released Windows 2000, known during its development cycle as Windows NT 5.0, in February 2000. It was successfully deployed both on the server and the workstation markets. Amongst Windows 2000’s most significant new features was Active Directory, a near-complete replacement of the NT 4.0 Windows Server domain model, which built on industry-standard technologies like DNS, LDAP, and Kerberos to connect machines to one another. Terminal Services, previously only available as a separate edition of NT 4, was expanded to all server versions.
A number of features from Windows 98 were incorporated as well, such as an improved Device Manager, Windows Media Player, and a revised DirectX that made it possible for the first time for many modern games to work on the NT kernel. Windows 2000 is also the last NT-kernel Windows operating system to lack Product Activation.
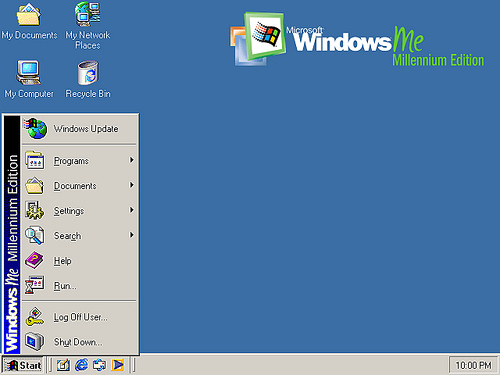
Windows Me (2000)
Windows Millennium Edition, or Windows Me, is a hybrid 16-bit/32-bit graphical operating system released on September 14, 2000 by Microsoft.
Windows Me was the successor to Windows 98 and, just like Windows 98, was targeted specifically at home PC users. It included Internet Explorer 5.5, Windows Media Player 7, and the new Windows Movie Maker software, which provided basic video editing and was designed to be easy for home users. Microsoft also updated the graphical user interface and the shell features and Windows Explorer in Windows Me with some of those first introduced in Windows 2000, which had been released as a business oriented operating system seven months earlier.
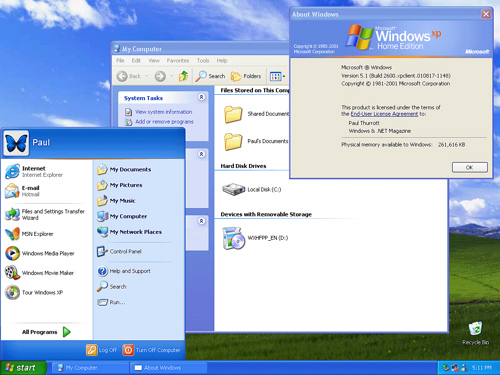
Windows XP (2001)
Windows XP was first released on October 25, 2001, and over 400 million copies were in use in January 2006, according to an estimate in that month by an IDC analyst. The name “XP” is short for “eXPerience” it’s the successor to both Windows 2000 Professional and Windows Me.
At the end of August 2009, Windows XP is the most widely used operating system in the world with a 66.2% market share, having peaked at 76.1% in January 2007. According to a Net Applications report, the Windows XP market share peaked as high as 85.3% in December 2006.
Windows XP features a new task-based graphical user interface. The Start menu and Windows indexing service were redesigned and many visual effects were added.
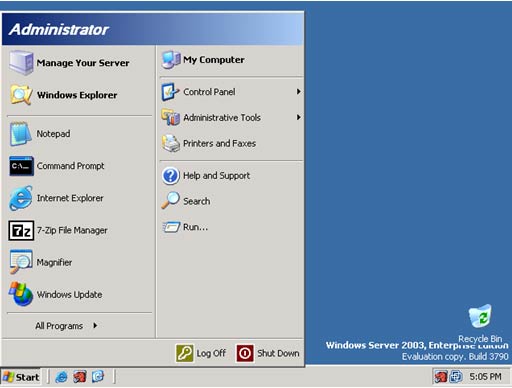
Windows Server 2003 (2003)
Windows Server 2003 (also referred to as Win2K3) is a server operating system produced by Microsoft. Introduced on 24 April 2003 as the successor to Windows 2000 Server, it is considered by Microsoft to be the cornerstone of its Windows Server System line of business server products
Windows Server 2003 comes in a number of editions, each targeted towards a particular size and type of business. In general, all variants of Windows Server 2003 have the ability to share files and printers, act as an application server, and host message queues, provide email services, authenticate users, act as an X.509 certificate server, provide LDAP directory services, serve streaming media, and to perform other server-oriented functions.
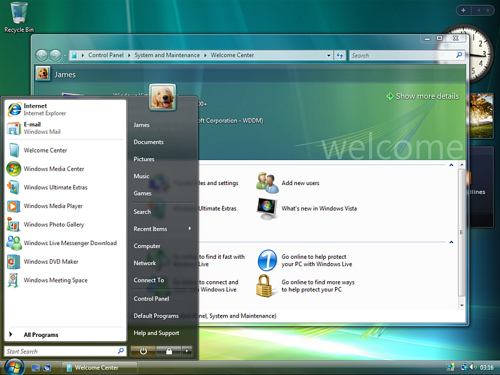
Windows Vista (2007)
On January 30, 2007, Windows Vista was released worldwide, and was made available for purchase and download from Microsoft’s website. The release of Windows Vista came more than five years after the introduction of its predecessor, Windows XP, the longest time span between successive releases of Microsoft Windows desktop operating systems.
Windows Vista contains many changes and new features, including an updated graphical user interface and visual style dubbed Windows Aero, a redesigned search function, multimedia tools including Windows DVD Maker, and redesigned networking, audio, print, and display sub-systems. Vista aims to increase the level of communication between machines on a home network, using peer-to-peer technology to simplify sharing files and digital media between computers and devices. Windows Vista includes version 3.0 of the .NET Framework, allowing software developers to write applications without traditional Windows APIs.
Microsoft’s primary stated objective with Windows Vista has been to improve the state of security in the Windows operating system. One common criticism of Windows XP and its predecessors is their commonly exploited security vulnerabilities and overall susceptibility to malware, viruses and buffer overflows.
At the end of August 2009, Windows Vista (with approximately 380 million users) is the second most widely used operating system in the world with an approx. 23% market share, the most widely used being Windows XP with an approx. 66% market share.
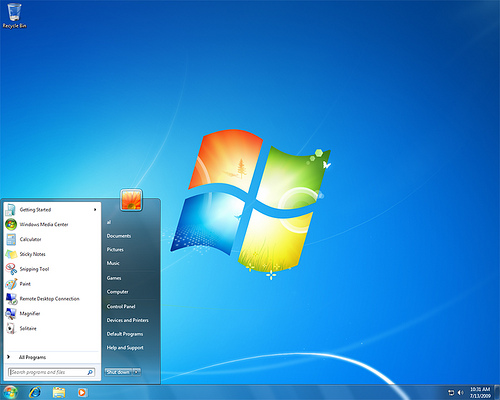
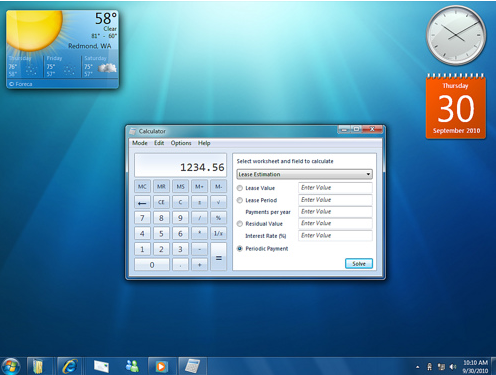
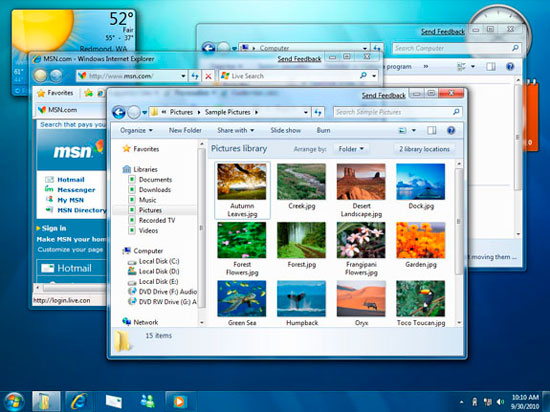
Windows 7 (2009)
Windows 7 (formerly codenamed Blackcomb and Vienna) is the latest version of Microsoft Windows. Windows 7 was released to manufacturing on July 22, 2009, with general retail availability set for October 22, 2009, less than three years after the release of its predecessor, Windows Vista.
Unlike its predecessor, which introduced a large number of new features, Windows 7 is intended to be a more focused, incremental upgrade to the Windows line, with the goal of being fully compatible with applications and hardware with which Windows Vista is already compatible. Presentations given by Microsoft in 2008 focused on multi-touch support, a redesigned Windows Shell with a new taskbar, a home networking system called HomeGroup, and performance improvements. Some applications that have been included with prior releases of Microsoft Windows, including Windows Calendar, Windows Mail, Windows Movie Maker, and Windows Photo Gallery, will not be included in Windows 7; some will instead be offered separately as part of the free Windows Live Essentials suite.
Acknowledgement: Wikipedia